If you are working on Kubernetes or interested in Kubernetes then you should know what are the essential and important configurations available on your cluster.
Let's explore the Kubernetes configurations and where they are stored.
Control Plane Components
API Server Configuration
Various components are available on the cluster, they need to communicate, and this server will act as a gateway for the communication.
This control plane component runs as a Static Pod on Kubernetes and you can find the manifest on.
vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml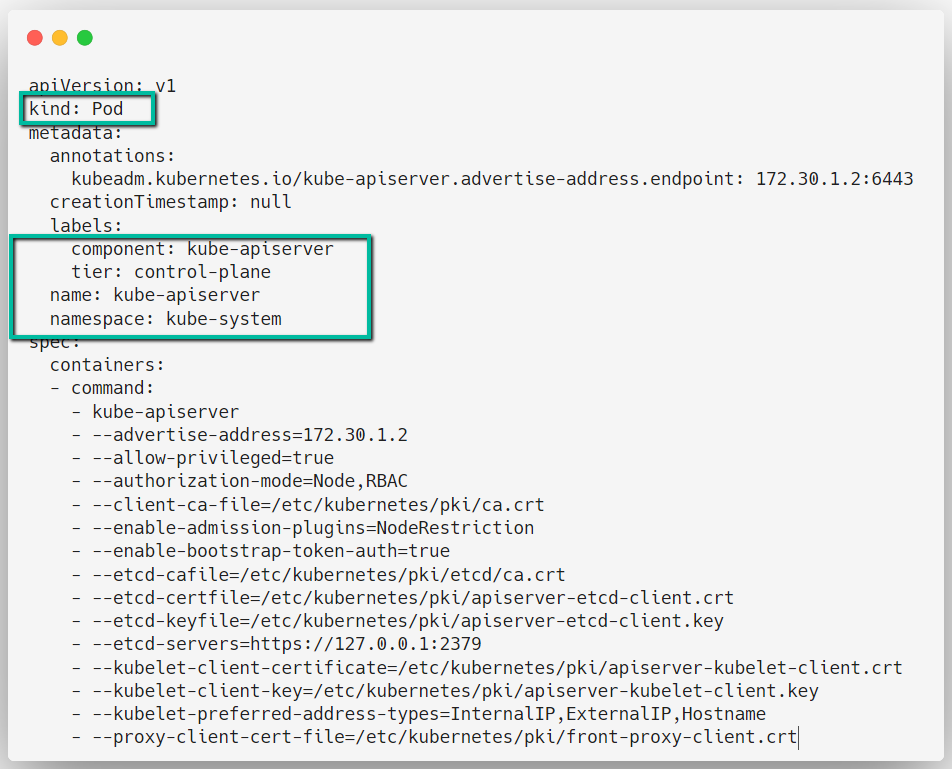
Controller Manager Configuration
In Kubernetes, many controllers are available such as namespace controller, service account controller, etc.
These controllers watch the intended resources and make changes if necessary, but someone needs to manage the controllers and the Controller Manager will do the job.
vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml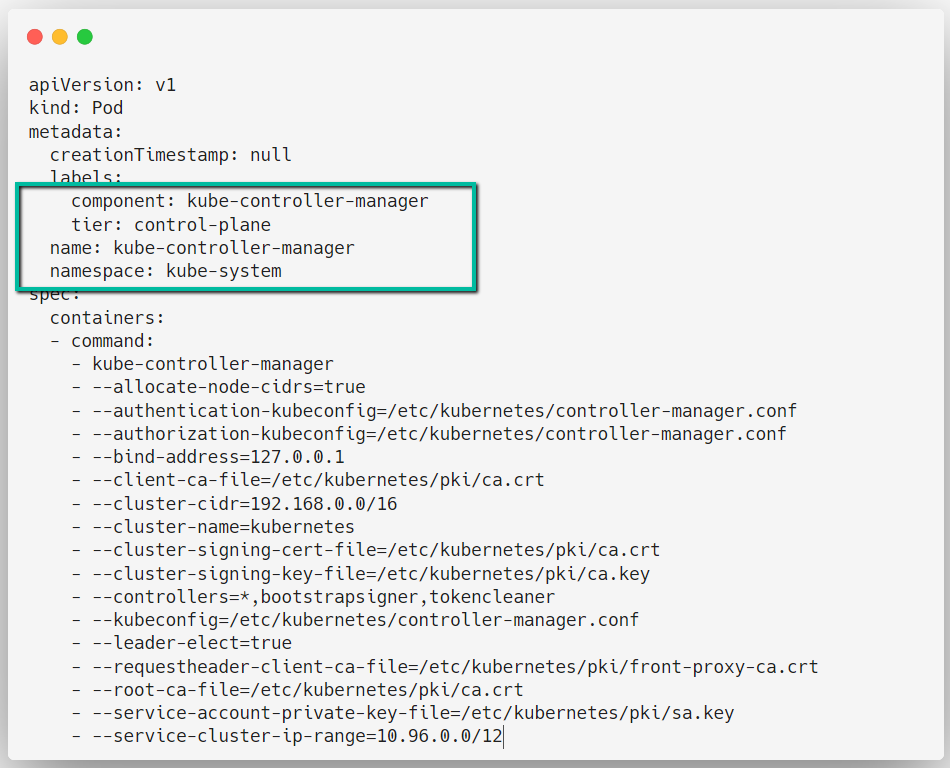
Scheduler Configuration
When you deploy a Pod, the Scheduler will decide in which Node the Pod should placed.
vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler.yaml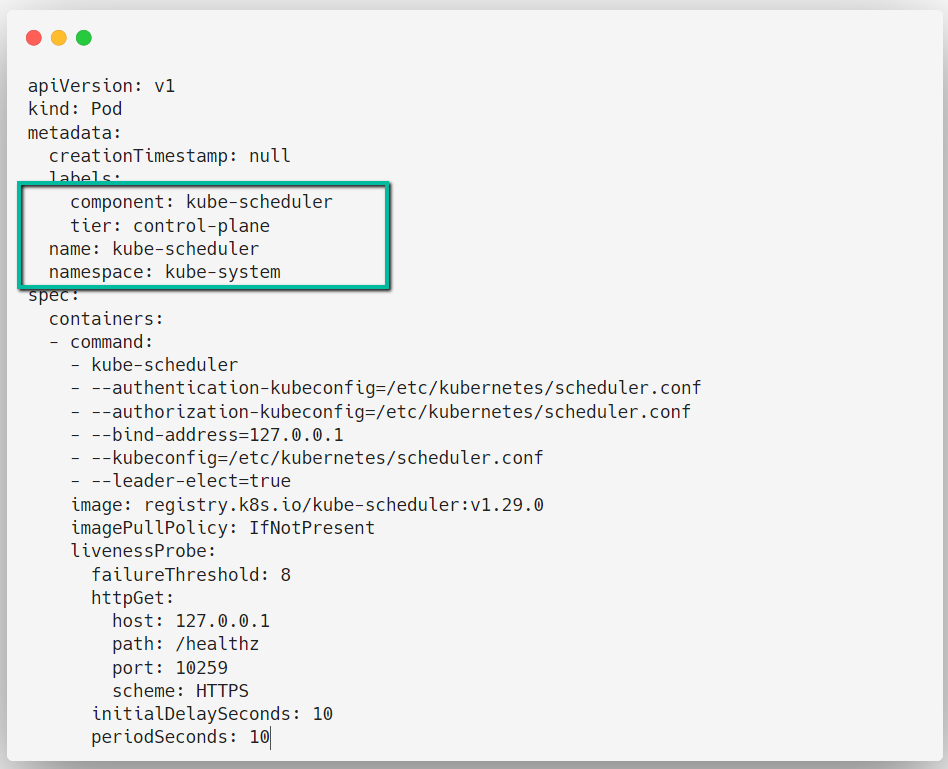
ETCD Configuration
This component will store all the cluster data in a key-value format.
vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml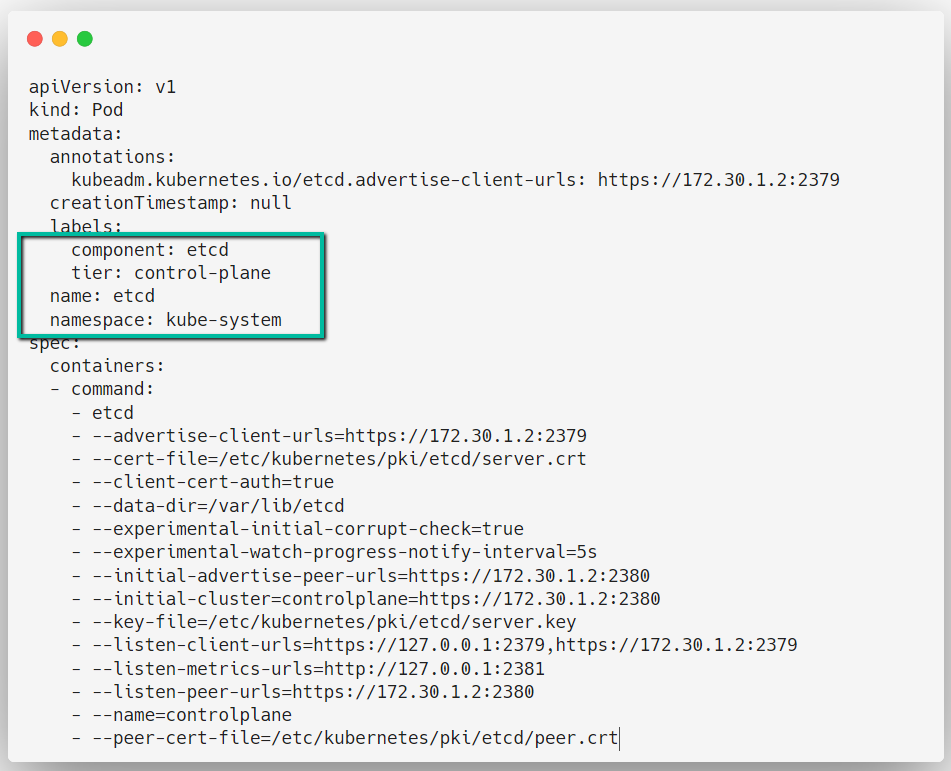
TLS Certificates
One major component that helps to communicate the Kubernetes components each other is TLS certification.
These certificates are created by a Certificate Authority (CA) which is already available on the Kubernetes.
If you want to see them, open the /etc/kubernetes/pki directory, and you can see all the available certificates.
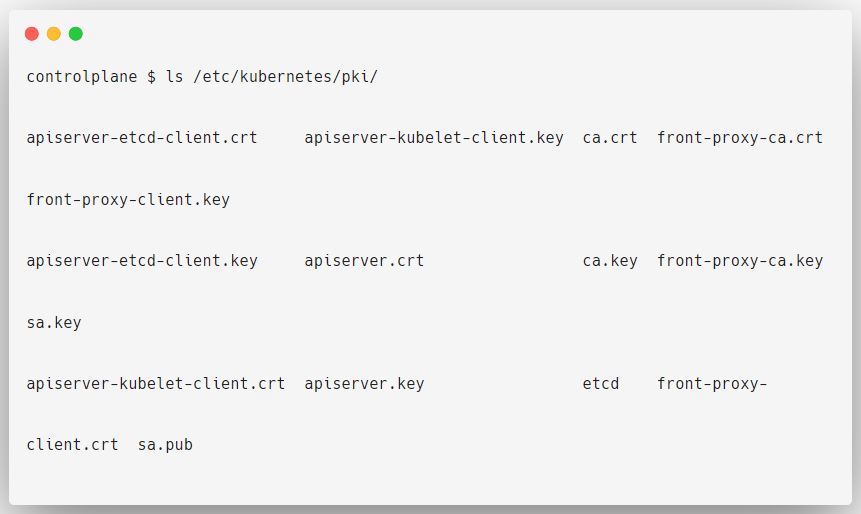
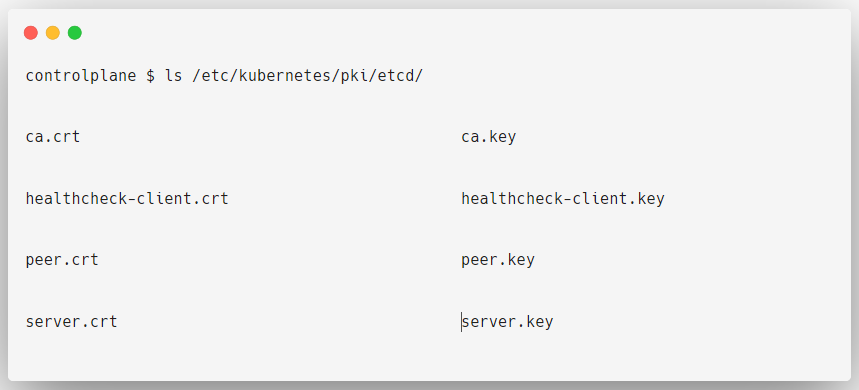
Along with these certificates, you can see a directory etcd, that also has certificates, which is related to the ETCD key-value store.
Kubeconfig Files
If a Kubernetes component wants to interact with the Kubernetes API server, a kubeconfig file is necessary.
Various kubeconfig files are available in each cluster and you can view them in /etc/kubernetes directory.
Admin Kubeconfig
As the name suggests this is the administrator configuration file. with the help of this, we can operate our Kubernetes cluster.
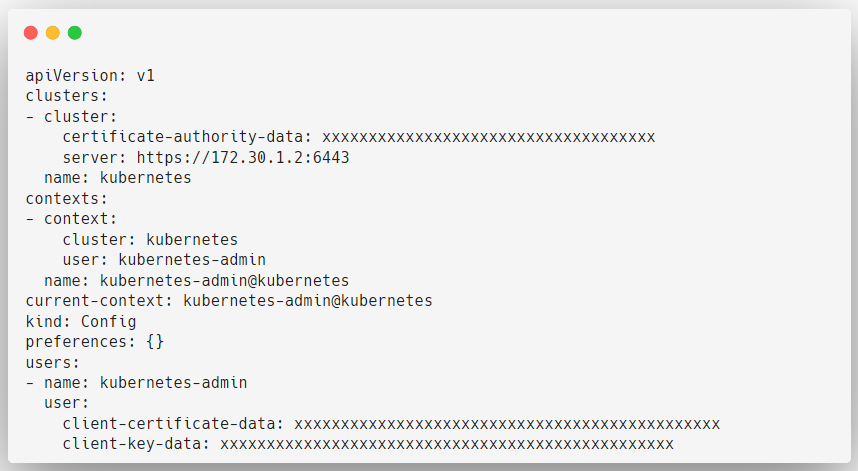
Here, server: https://172.30.1.2:6443 is the endpoint of the API server.
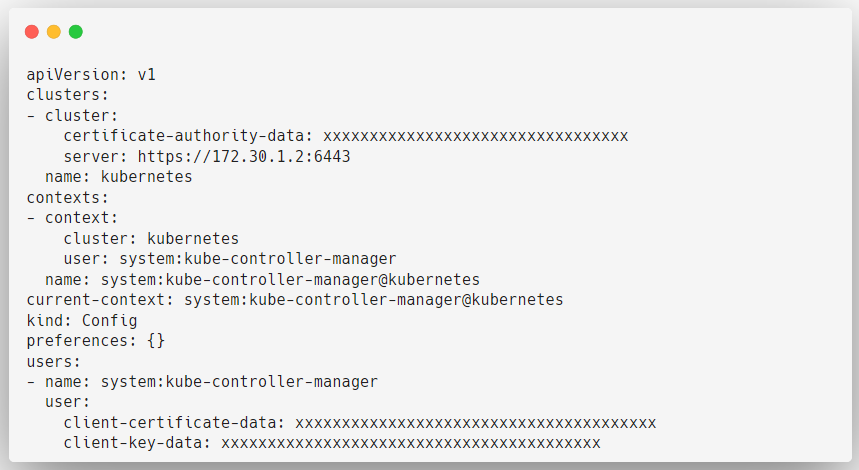
Controller Manager Kubeconfig
We use various types of controllers on Kubernetes, but the controller manager actually manages all the controllers on the cluster.
The controller manager needs to keep watch of these controllers, for that API Server interaction is necessary so for that this configuration is necessary.
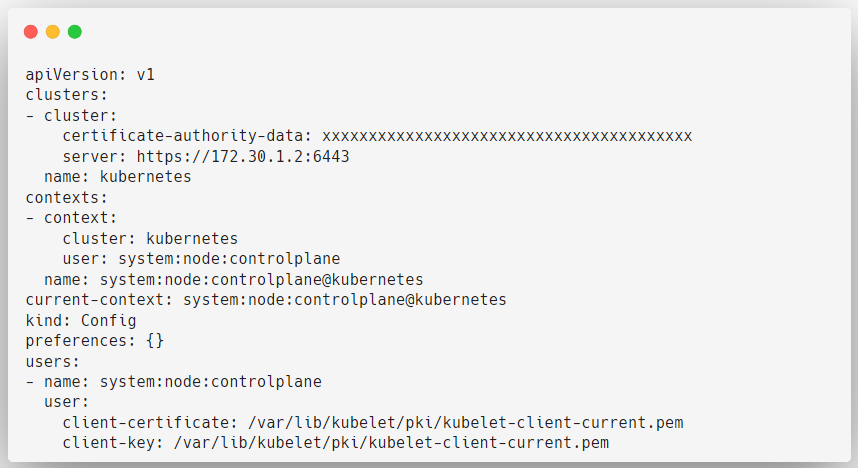
Kubelet Kubeconfig
One of the common components that is available on the Control plane and worker node is the Kubelet, this will do many jobs on Nodes so it definitely has to interact with the API server. For that, this configuration is required.
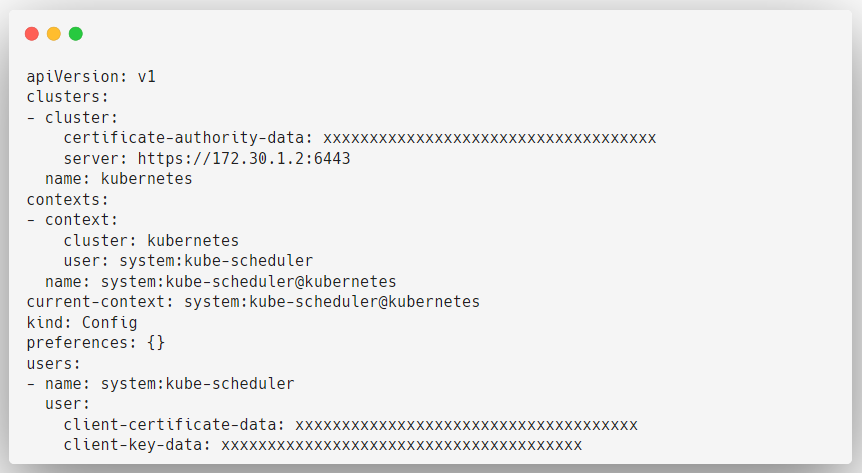
Scheduler Kubeconfig
This is the component that decides where the Pod has to be placed. for that, it has to interact with the API Server.
Conclusion
There are more configurations available on Kubernetes but these are the essential configuration files.
Understanding these files will help you troubleshoot in real-use cases also if you are preparing for CNCF exams like CKA or CKS you might face questions related to troubleshooting scenarios.
